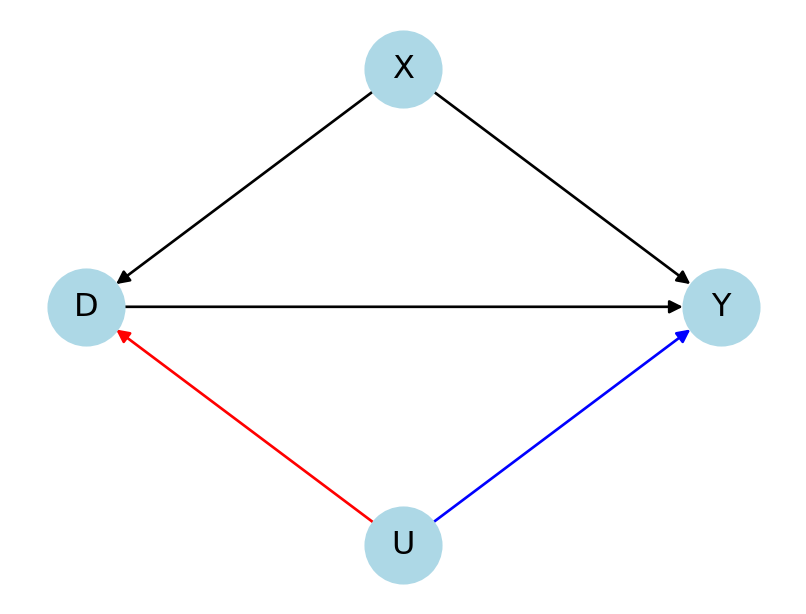
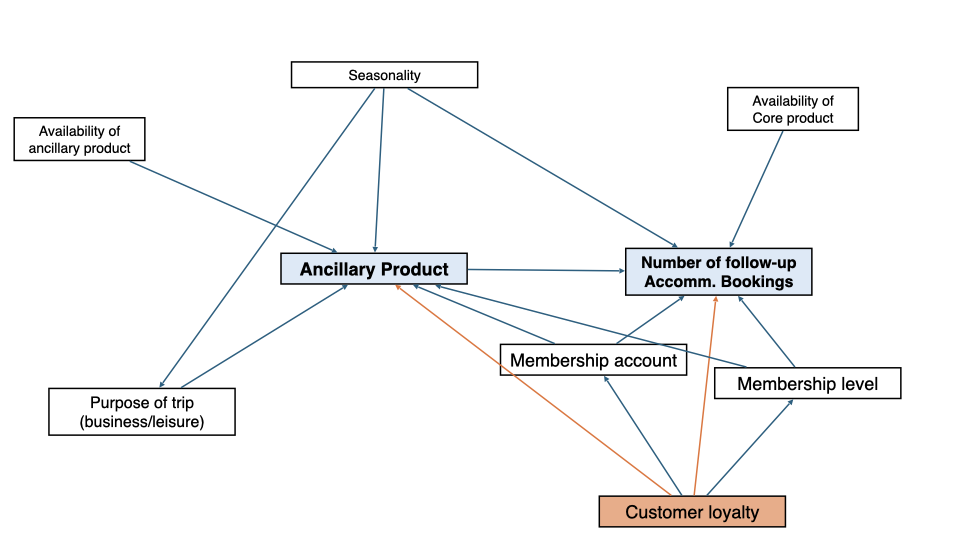
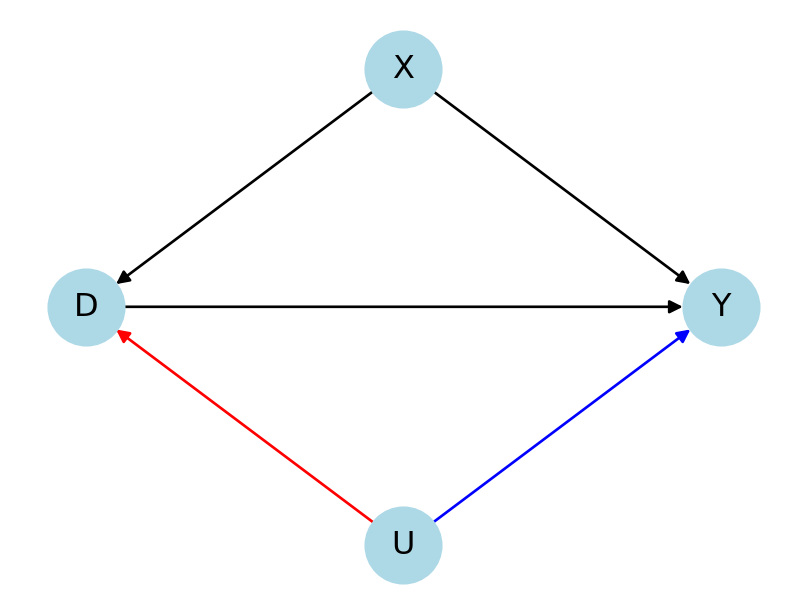
Bach, Philipp, Victor Chernozhukov, Carlos Cinelli, Lin Jia, Sven Klaassen, Nils Skotara, and Martin Spindler. 2024. “Sensitivity Analysis for Causal ML: A Use Case at Booking.com.” In Proceedings of the KDD’24 Workshop on Causal Inference and Machine Learning in Practice.
Bach, Philipp, Victor Chernozhukov, Malte S Kurz, and Martin Spindler. 2022. “DoubleML-an Object-Oriented Implementation of Double Machine Learning in Python.” Journal of Machine Learning Research 23: 53–51.
Bach, Philipp, Malte S. Kurz, Victor Chernozhukov, Martin Spindler, and Sven Klaassen. 2024.
“DoubleML: An Object-Oriented Implementation of Double Machine Learning in R.” Journal of Statistical Software.
https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v108.i03.
Blackwell, Matthew. 2013. “A Selection Bias Approach to Sensitivity Analysis for Causal Effects.” Political Analysis 22 (2): 169–82.
Brumback, Babette A, Miguel A Hernán, Sebastien JPA Haneuse, and James M Robins. 2004. “Sensitivity Analyses for Unmeasured Confounding Assuming a Marginal Structural Model for Repeated Measures.” Statistics in Medicine 23 (5): 749–67.
Carnegie, Nicole Bohme, Masataka Harada, and Jennifer L Hill. 2016. “Assessing Sensitivity to Unmeasured Confounding Using a Simulated Potential Confounder.” Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness 9 (3): 395–420.
Chernozhukov, Victor, Denis Chetverikov, Mert Demirer, Esther Duflo, Christian Hansen, Whitney Newey, and James Robins. 2018.
“Double/Debiased Machine Learning for Treatment and Structural Parameters.” The Econometrics Journal 21 (1): C1–68.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/ectj.12097.
Chernozhukov, Victor, Carlos Cinelli, Whitney Newey, Amit Sharma, and Vasilis Syrgkanis. 2022.
“Long Story Short: Omitted Variable Bias in Causal Machine Learning.” National Bureau of Economic Research.
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2112.13398.
Chernozhukov, Victor, Christian Hansen, Nathan Kallus, Martin Spindler, and Vasilis Syrgkanis. forthcoming.
Applied Causal Inference Powered by ML and AI. online.
https://causalml-book.org/.
Chernozhukov, Victor, Whitney K Newey, and Rahul Singh. 2022. “Automatic Debiased Machine Learning of Causal and Structural Effects.” Econometrica 90 (3): 967–1027.
Cinelli, Carlos, Jeremy Ferwerda, and Chad Hazlett. 2020. “Sensemakr: Sensitivity Analysis Tools for OLS in r and Stata.” Available at SSRN 3588978.
Cinelli, Carlos, and Chad Hazlett. 2020. “Making Sense of Sensitivity: Extending Omitted Variable Bias.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology 82 (1): 39–67.
———. 2022. “An Omitted Variable Bias Framework for Sensitivity Analysis of Instrumental Variables.” Available at SSRN 4217915.
Cinelli, Carlos, Daniel Kumor, Bryant Chen, Judea Pearl, and Elias Bareinboim. 2019. “Sensitivity Analysis of Linear Structural Causal Models.” International Conference on Machine Learning.
Cornfield, Jerome, William Haenszel, E Cuyler Hammond, Abraham M Lilienfeld, Michael B Shimkin, and Ernst L Wynder. 1959. “Smoking and Lung Cancer: Recent Evidence and a Discussion of Some Questions.” Journal of National Cancer Institute, no. 23: 173–203.
Dorie, Vincent, Masataka Harada, Nicole Bohme Carnegie, and Jennifer Hill. 2016. “A Flexible, Interpretable Framework for Assessing Sensitivity to Unmeasured Confounding.” Statistics in Medicine 35 (20): 3453–70.
Frank, Kenneth A. 2000. “Impact of a Confounding Variable on a Regression Coefficient.” Sociological Methods & Research 29 (2): 147–94.
Frank, Kenneth A, Spiro J Maroulis, Minh Q Duong, and Benjamin M Kelcey. 2013. “What Would It Take to Change an Inference? Using Rubin’s Causal Model to Interpret the Robustness of Causal Inferences.” Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis 35 (4): 437–60.
Frank, Kenneth A, Gary Sykes, Dorothea Anagnostopoulos, Marisa Cannata, Linda Chard, Ann Krause, and Raven McCrory. 2008. “Does NBPTS Certification Affect the Number of Colleagues a Teacher Helps with Instructional Matters?” Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis 30 (1): 3–30.
Hosman, Carrie A, Ben B Hansen, and Paul W Holland. 2010. “The Sensitivity of Linear Regression Coefficients’ Confidence Limits to the Omission of a Confounder.” The Annals of Applied Statistics, 849–70.
Imai, Kosuke, Luke Keele, Teppei Yamamoto, et al. 2010. “Identification, Inference and Sensitivity Analysis for Causal Mediation Effects.” Statistical Science 25 (1): 51–71.
Imbens, Guido W. 2003. “Sensitivity to Exogeneity Assumptions in Program Evaluation.” The American Economic Review 93 (2): 126–32.
Middleton, Joel A, Marc A Scott, Ronli Diakow, and Jennifer L Hill. 2016. “Bias Amplification and Bias Unmasking.” Political Analysis 24 (3): 307–23.
Oster, Emily. 2017. “Unobservable Selection and Coefficient Stability: Theory and Evidence.” Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 1–18.
Robins, James M. 1999. “Association, Causation, and Marginal Structural Models.” Synthese 121 (1): 151–79.
Rosenbaum, Paul R. 2002. “Observational Studies.” In Observational Studies, 1–17. Springer.
Vanderweele, Tyler J., and Onyebuchi A. Arah. 2011.
“Bias formulas for sensitivity analysis of unmeasured confounding for general outcomes, treatments, and confounders.” Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass.) 22 (1): 42–52.
https://doi.org/10.1097/ede.0b013e3181f74493.
Zhang, Chi, Carlos Cinelli, Bryant Chen, and Judea Pearl. 2021. “Exploiting Equality Constraints in Causal Inference.” In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, 1630–38. PMLR.